


While about 32 of the chemical elements occur on Earth in native uncombined form, most of these occur as mixtures. All but a few of the most inert elements, such as noble gases and noble metals, are usually found on Earth in chemically combined form, as chemical compounds. While all of the 98 naturally occurring elements have been identified in mineral samples from Earth's crust, only a small minority of elements are found as recognizable, relatively pure minerals.Īmong the more common of such "native elements" are copper, silver, gold, carbon (as coal, graphite, or diamonds), sulfur, and mercury. Relatively pure samples of isolated elements are uncommon in nature. However, chemical bonding of many types of elements results in crystalline solids and metallic alloys for which exact chemical formulas do not exist. Two thirds of the chemical elements occur naturally on Earth only as compounds, and in the remaining third, often the compound forms of the element are most common.Ĭhemical compounds may be composed of elements combined in exact whole-number ratios of atoms, as in water, table salt, and minerals such as quartz, calcite, and some ores. When two or more distinct elements are chemically combined, with the atoms held together by chemical bonds, the result is termed a chemical compound. Dark matter may also include normal baryonic matter and neutrinos. The remainder is believed to be dark matter, a range of substances whose composition is largely unknown and not composed of chemical elements, since it lacks protons, neutrons or electrons.
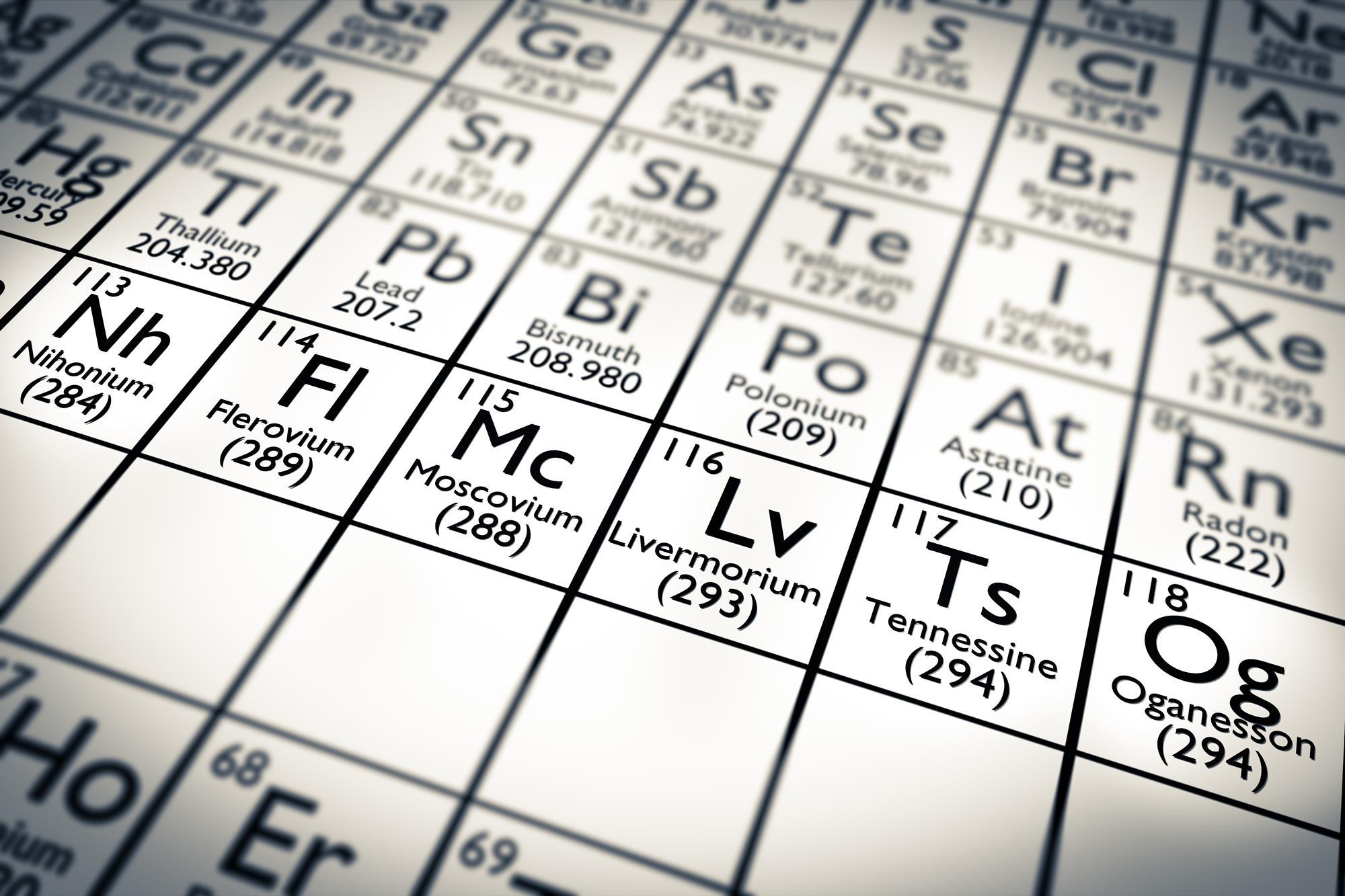

Although all known chemical matter is composed of these elements, chemical matter itself is hypothesized to constitute only about 15% of the matter in the universe. However, iron is the most abundant element (by mass) making up the Earth, and oxygen is the most common element in Earth's crust. Hydrogen and helium are by far the most abundant elements in the universe. Save for unstable radioactive elements with short half lives, all of the elements are available industrially, most of them in high degrees of purity. The properties of the chemical elements are often summarized using the periodic table, which organizes the elements by increasing atomic number into rows ("periods") in which the columns ("groups") share recurring ("periodic") physical and chemical properties. The history of the discovery and use of the elements began with primitive human societies that found native elements like copper and gold and extracted (smelted) iron and a few other metals from their ores.Īlchemists and chemists subsequently identified many more, with nearly all of the naturally-occurring elements becoming known by 1900. While most elements are generally stable, a small amount of natural transformation of one element to another also occurs in the decay of radioactive elements as well as other natural nuclear processes.Įarly history and eventual organisation of the elements The high abundance of oxygen, silicon, and iron on Earth reflects their common production in such stars. Production of heavier elements, from carbon to the very heaviest elements, proceeded by stellar nucleosynthesis, and these were made available for later solar system and planetary formation by planetary nebulae and supernovae, which blast these elements into space. The lightest chemical elements, including hydrogen, helium and smaller amounts of lithium, beryllium and boron, are thought to have been produced by various cosmic processes during the Big Bang and cosmic-ray spallation. image: adapted from wikipediaĮlements are divided into metals, metalloids, and non-metals.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
